QubitApproximant
A python package for approximating quantum circuits with a single qubit.
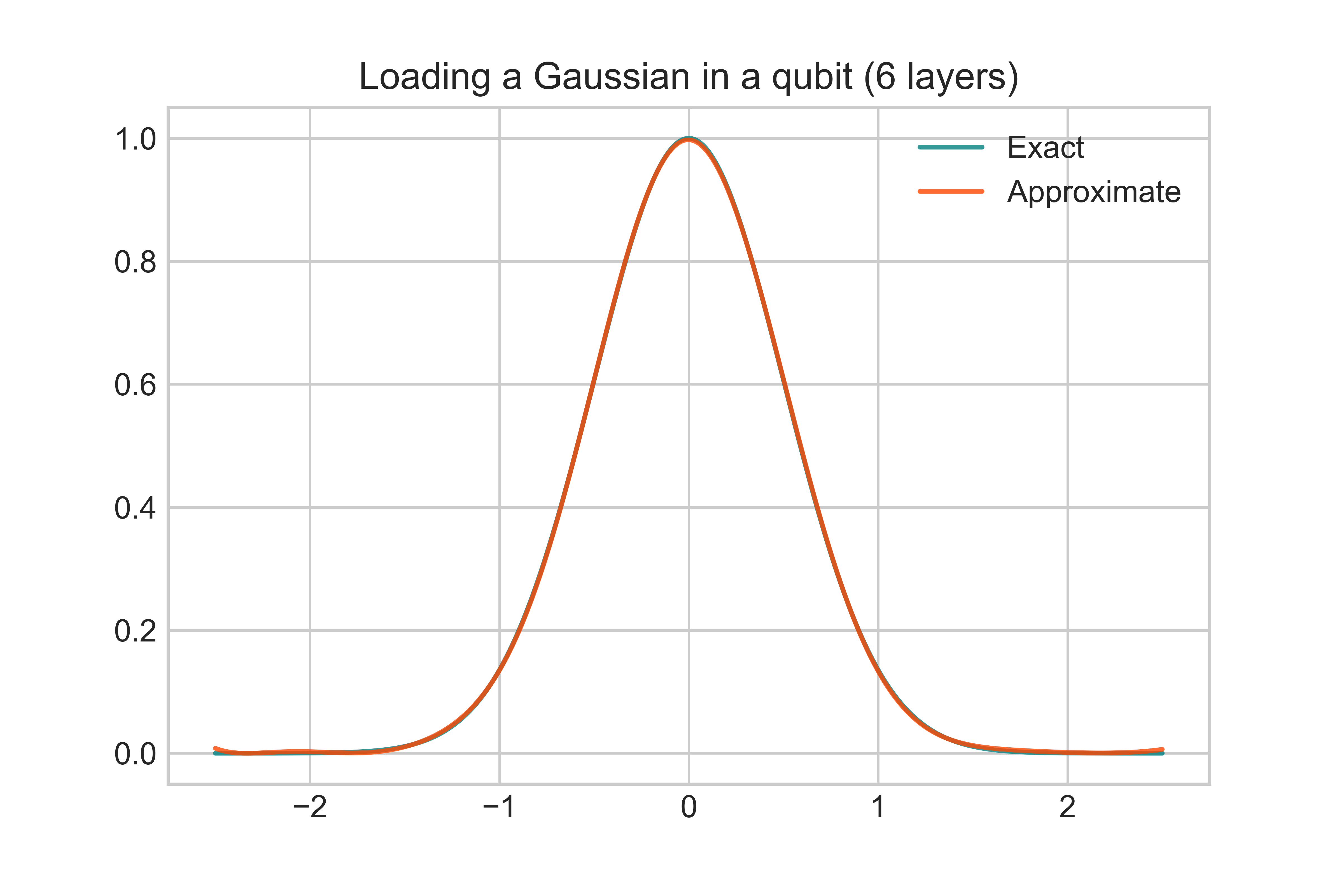
Documentation and examples
Documentation created with mkdocs can be found in https://pablovegan.github.io/QubitApproximant/.
Installation
With pip:
pip install qubit-approximant
Quick usage
Importing a function
In the submodule benchmarking.functions there are multiple test functions to choose from
import numpy as np
from qubit_approximant.benchmarking.functions import gaussian
x = np.linspace(-2.5, 2.5, 1000)
fn_kwargs = {'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.5, 'coef': 1}
fn = gaussian(x, **fn_kwargs)
Creating a circuit
To create a circuit just choose the ansaz (CircuitRxRyRz, CircuitRxRy or CircuitRy) and the encoding ('prob' or 'amp').
from qubit_approximant.core import CircuitRxRyRz
circuit = CircuitRxRyRz(x, encoding='prob')
Cost function
To find the optimum parameters of the circuit, we need to choose a cost function. This can be done with the Cost class, where we input the function to approximate, the circuit ansatz and a metric to quantify the error in the approximation (options are 'mse', 'rmse', 'mse_weighted', 'kl_divergence' or 'log_cosh')
from qubit_approximant.core import Cost
cost = Cost(fn, circuit, metric='mse')
Optimizer
Choose an optimizer (BlackBoxOptimizer, GDOptimizer or AdamOptimizer)
from qubit_approximant.core import BlackBoxOptimizer
optimizer = BlackBoxOptimizer(method="L-BFGS-B")
layers = 6
init_params = np.random.default_rng().standard_normal(4 * layers)
opt_params = optimizer(cost, cost.grad, init_params)
Multilayer optimizer
We may also optimize an ansatz for multiple layers using the LayerwiseOptimizer, which uses the optimum parameters for a circuit with $L$ layers as initial parameters for the optimization of a circuit with $L+1$ layers. A list with the optimum parameters for each layer is returned.
from qubit_approximant.core import LayerwiseOptimizer
layerwise_opt = LayerwiseOptimizer(
optimizer,
min_layer=3,
max_layer=7,
new_layer_coef=0.3,
new_layer_position='random'
)
params_list = layerwise_opt(cost, cost.grad, init_params)
Note: a MultilayerOptimizer which doesn't reuse the optimized parameters from previous layers is also available.
Error metrics
To benchmark the optimization we can use some common metrics, like the $L^1$ norm, $L^2$ norm, $L^\infty$ norm or infidelity $1-F$, to compare the function encoded in the circuit with the desired function. Following our example, fn is a gaussian:
l1_list, l2_list, inf_list, infidelity_list = metric_results(
params_list,
circuit,
fn = gaussian,
fn_kwargs = {'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.5, 'coef': 1}
)
Wrapping up
Test the library yourself!
import numpy as np
from qubit_approximant.benchmarking.functions import gaussian
from qubit_approximant.core import CircuitRxRyRz, Cost, BlackBoxOptimizer, LayerwiseOptimizer
from qubit_approximant.benchmarking import metric_results
x = np.linspace(-2.5, 2.5, 1000)
fn_kwargs = {'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.5, 'coef': 1}
fn = gaussian(x, **fn_kwargs)
circuit = CircuitRxRyRz(x, encoding='prob')
cost = Cost(fn, circuit, metric='mse')
optimizer = BlackBoxOptimizer(method="L-BFGS-B")
min_layer = 3
init_params = np.random.default_rng().standard_normal(4 * min_layer)
layerwise_opt = LayerwiseOptimizer(
optimizer,
min_layer=min_layer,
max_layer=7,
new_layer_coef=0.3,
new_layer_position='random'
)
params_list = layerwise_opt(cost, cost.grad, init_params)
l1_list, l2_list, inf_list, infidelity_list = metric_results(
fn=gaussian,
fn_kwargs={'mean': 0.0, 'std': 0.5, 'coef': 1},
circuit=circuit,
params_list=params_list
)
Bonus: benchmarking multiple initial parameters
The initial paramenters for the optimizer are generated at random with a seed of our choice. We can benchmark the optimizer against multiple seeds (since it is a time consuming task it is parallelized using mpi).
benchmark_seeds(
num_seeds = 4,
fn = gaussian,
fn_kwargs = fn_kwargs,
circuit = circuit,
cost = cost,
optimizer = multilayer_opt,
filename = "results",
)
References
This library is based on Adrian Pérez Salinas article Data re-uploading for a universal quantum classifier.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
License
This software is under the GNU General Public License v3.0.




